Don't hesitate to send a message
The design and production comply with ISO8537. The plastic parts are moulded by ...
Medical injection tools play an important role in daily treatment routines across global healthcare environments. The Insulin Syringe remains a widely used device designed for precise insulin administration. For medical distributors and device integrators, product consistency and structural stability are common concerns during sourcing and application.
From a manufacturing perspective, an Insulin Syringe must combine reliable material selection, dimensional precision, and controlled assembly processes. Patients and healthcare professionals often focus on smooth injection experiences, accurate scale markings, and comfortable handling. Manufacturers respond to these expectations by refining needle processing, barrel transparency, and plunger flexibility.

Factories that specialize in medical injection products focus heavily on automated production lines and validated testing procedures. These systems help maintain product uniformity across different production batches, supporting healthcare providers that require stable supply channels.
Material selection directly influences product performance and durability. Medical-grade polypropylene is commonly used for syringe barrels due to its transparency and chemical stability. Stainless steel is typically selected for needle production, offering strength and resistance to corrosion.
Professional Insulin Syringe Suppliers often implement raw material testing before entering the production stage. Material inspection involves mechanical testing, dimensional analysis, and surface evaluation. This process helps maintain structural consistency throughout production cycles.
Additionally, silicone lubrication is applied to internal barrel surfaces to improve plunger movement. Controlled lubrication supports smooth injection action, reducing resistance during operation. This manufacturing detail is particularly valuable when syringes are used repeatedly in routine treatment settings.
Injection accuracy is closely linked to scale printing clarity and barrel calibration. A high-quality Insulin Syringe requires precise graduation markings that remain visible during usage. Manufacturers use automated printing technology combined with optical inspection to verify measurement alignment.
Needle grinding and electro-polishing also contribute to injection performance. These processes refine the needle tip geometry and surface smoothness. Consistent needle shaping helps maintain stable penetration performance during injection procedures.
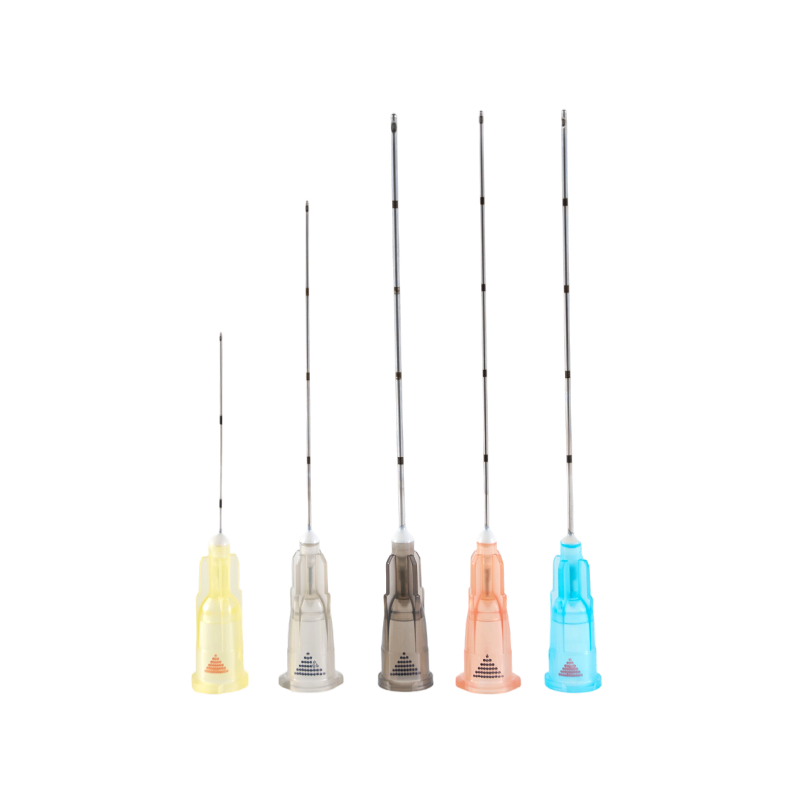

Experienced Insulin Syringe Suppliers utilize digital measurement systems to verify needle wall thickness and tip angle. These monitoring technologies help maintain dimensional uniformity across large production volumes while reducing manual error.
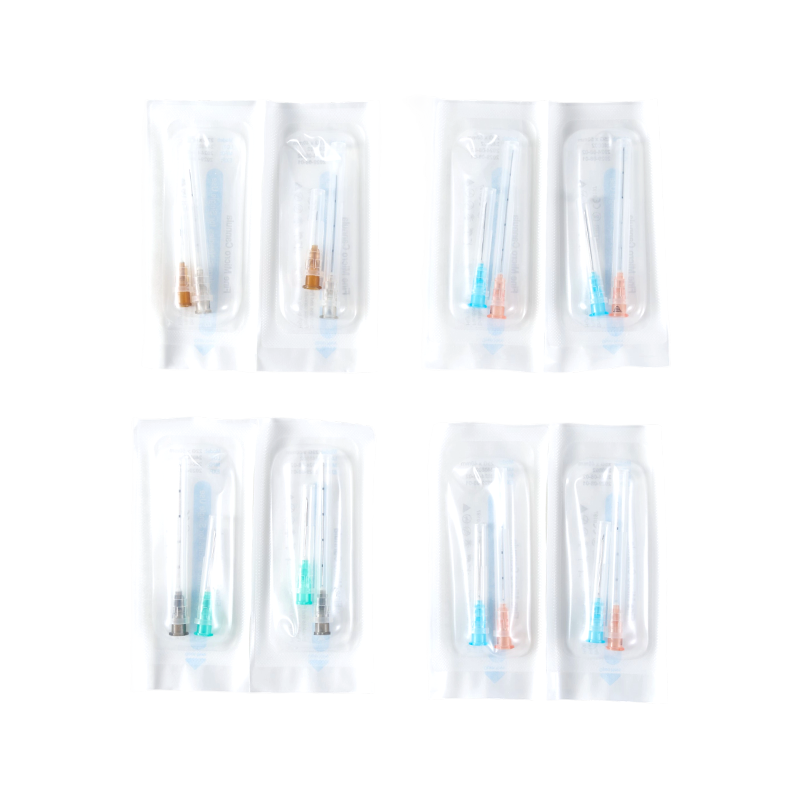
Packaging is often overlooked but plays a significant role in product protection during transportation and storage. Medical syringes are commonly sealed in blister packs or polyethylene packaging, which helps maintain cleanliness and structural integrity.
A well-designed packaging process prevents mechanical deformation and environmental contamination. Insulin Syringe Suppliers frequently conduct packaging seal strength testing and aging simulation studies. These procedures evaluate how packaging materials perform during extended storage or transportation conditions.
Experienced Insulin Syringe Suppliers focus on consistency, traceability, and adaptable design options to meet different application requirements while aligning with current manufacturing trends. Together, these factors show how structured production capabilities support long-term cooperation within the medical device supply chain.
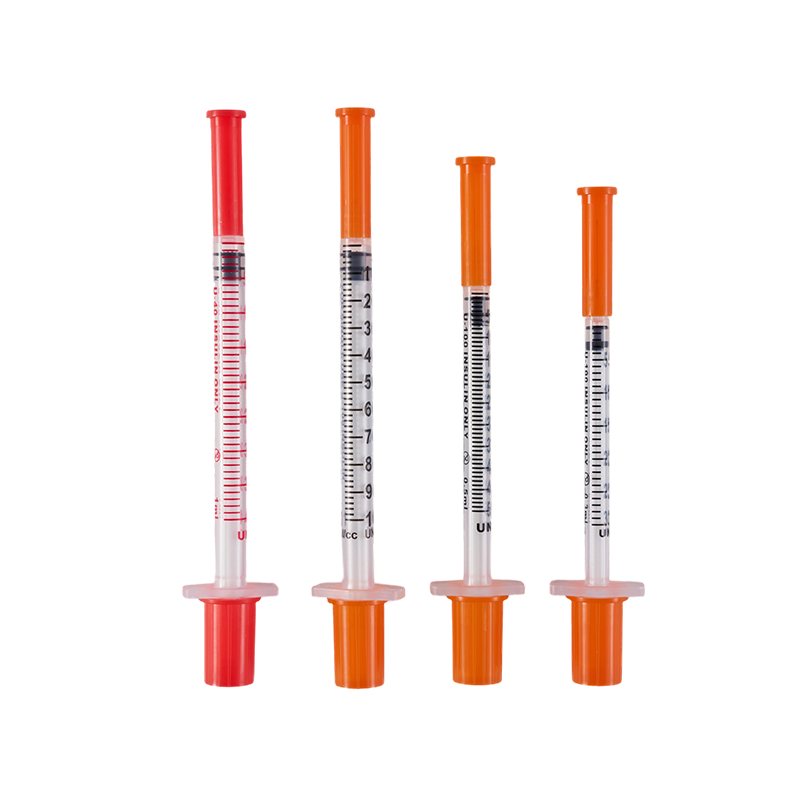
The design and production comply with ISO8537. The plastic parts are moulded by ...

There are three kinds of the tip types, Sealed-circle with 2 side holes, sealed-...
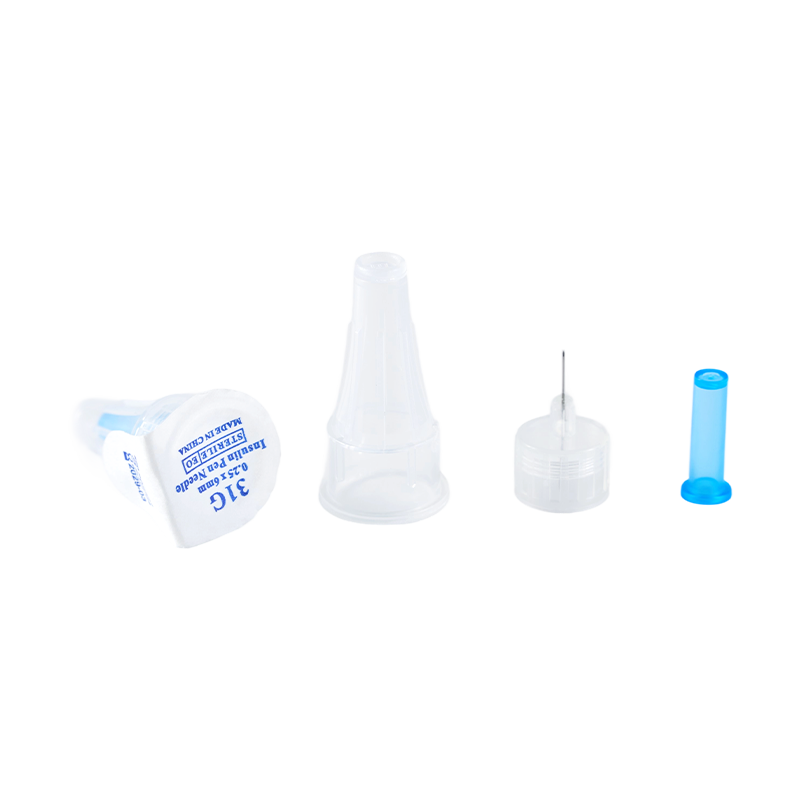

Assembling with insulin pen, for insulin hypodermic injection.The plastic parts ...
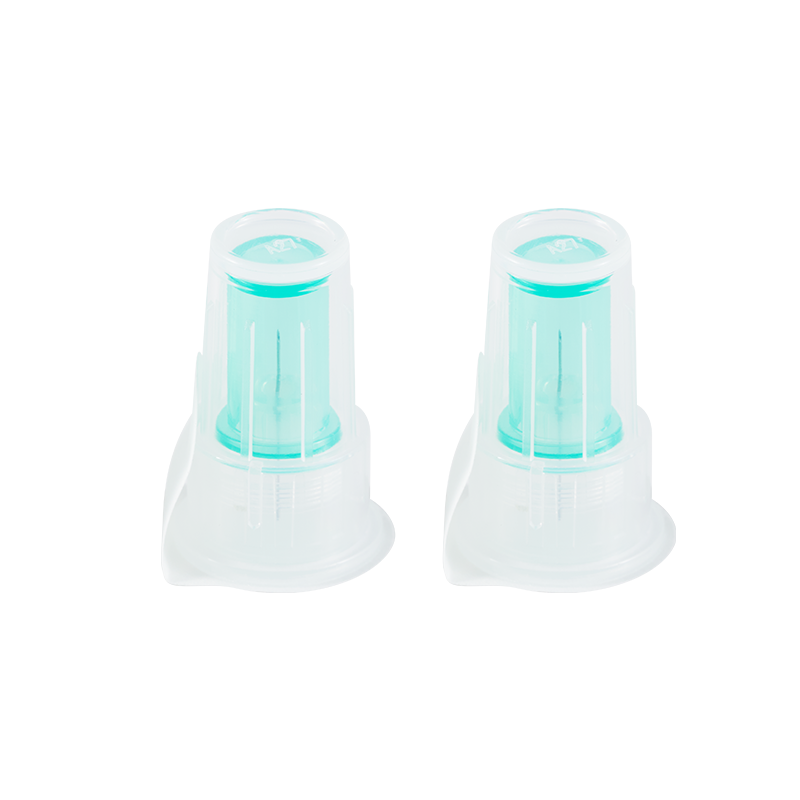

Used in conjunction with an insulin pen, it is used for subcutaneous injection o...
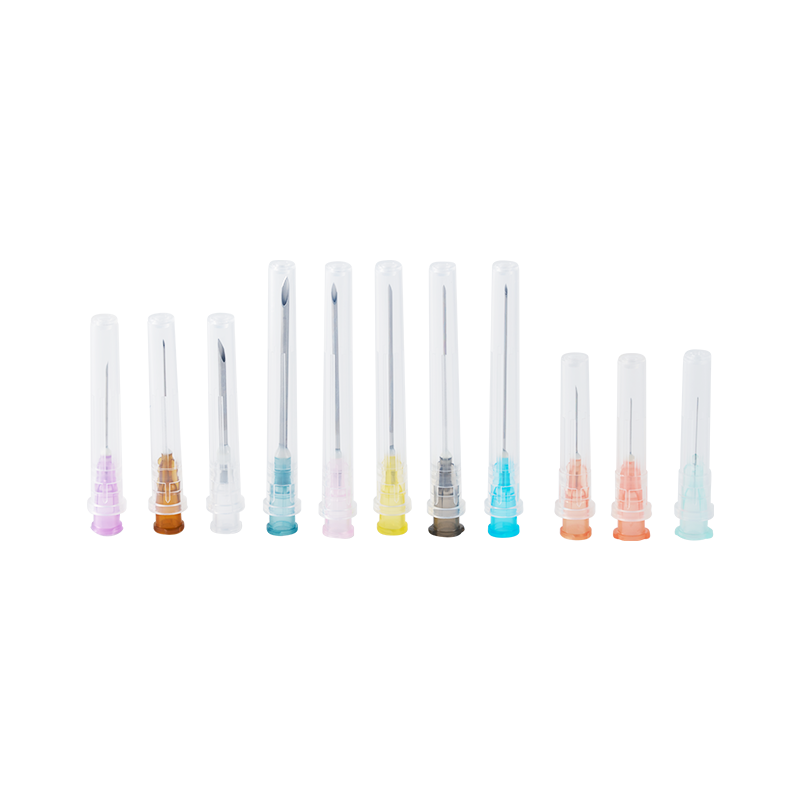

The cannula is made of high quality austenite stainless steel.All the components...
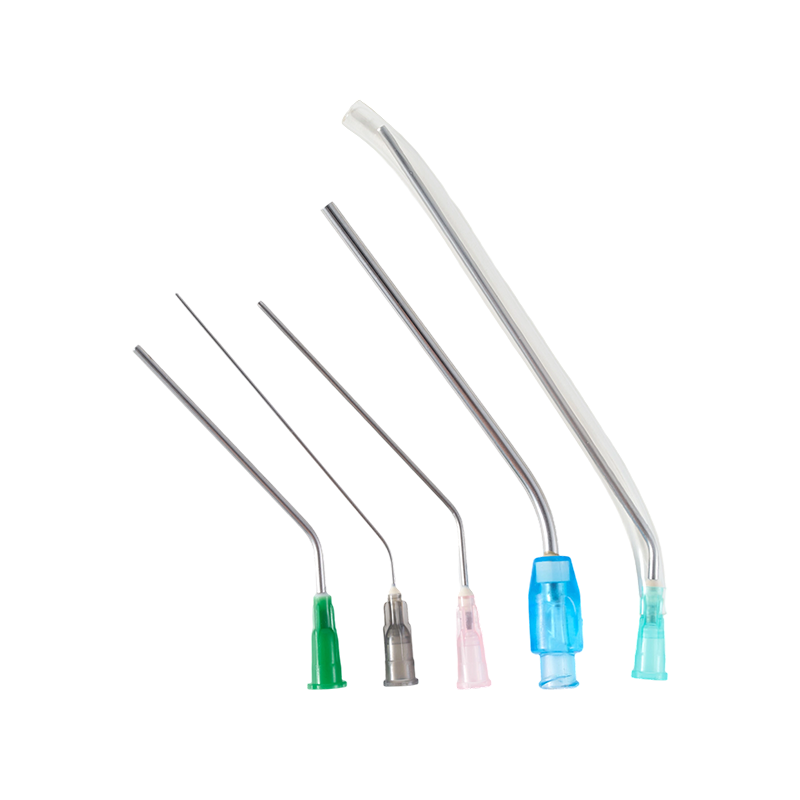
The material of the needle is Medical grade SUS304,which have great stiffness, t...
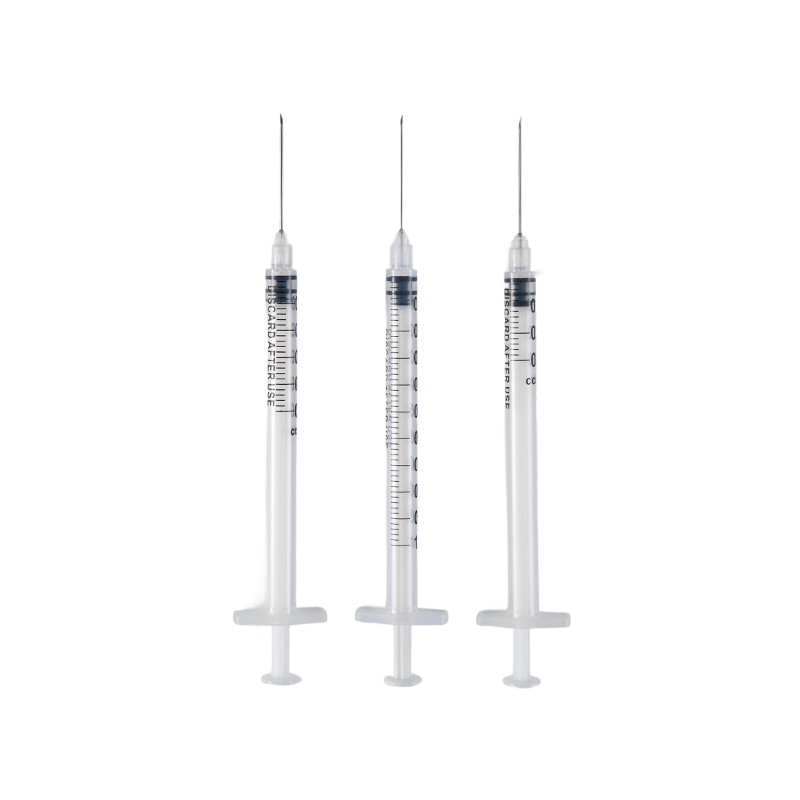
The barrel is made from high transparent polypropylene(PP),which have a bright a...
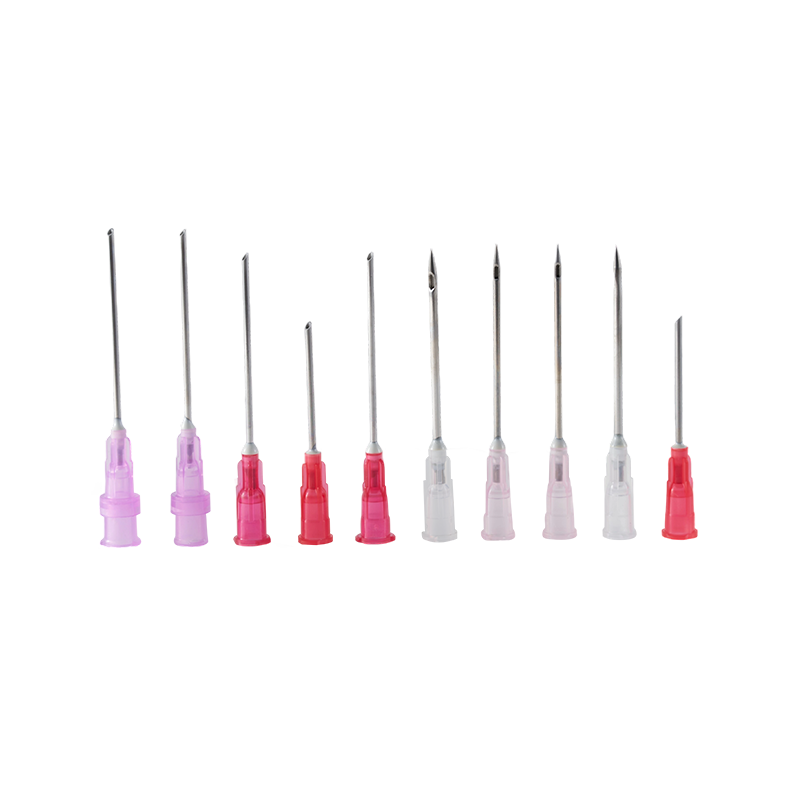

The cannula is made of high quality austenite stainless steel.The lancet tip is ...