Don't hesitate to send a message
The design and production comply with ISO8537. The plastic parts are moulded by ...
Proper storage of needles is a critical consideration for healthcare facilities, laboratories, and clinics. Improper handling or storage of Sterile Needles can compromise safety standards and increase operational challenges. Healthcare providers must follow best practices to maintain the sterility of Blood Collection Needles and other Medical Supplies Needles while ensuring accessibility for staff.
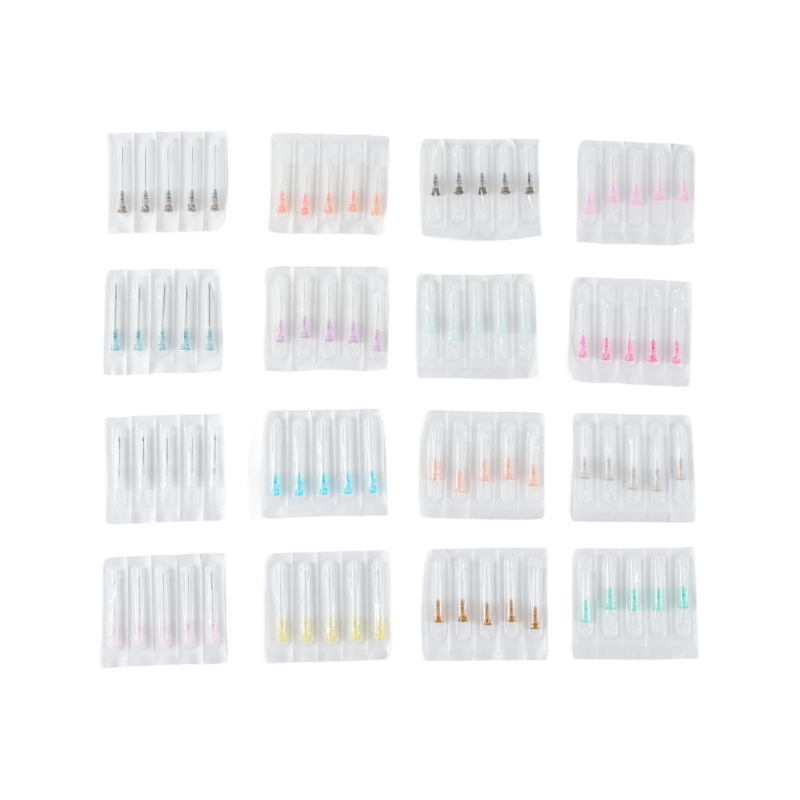

The storage area for Sterile Needles should be clean, dry, and temperature-controlled. Excessive humidity or extreme temperatures can affect packaging integrity and compromise the sterility of Blood Collection Needles. Clinics should designate specific cabinets or shelves exclusively for Medical Supplies Needles to minimize the risk of cross-contamination with other equipment or consumables.
Always keep Sterile Needles in their original packaging until use. Individual blister packs or sealed boxes help preserve sterility and reduce exposure to environmental contaminants. Blood Collection Needle packs should remain sealed and only opened when needed, preventing accidental contamination. Maintaining packaging integrity also aids in inventory management of Medical Supplies Needles.
To avoid using outdated Sterile Needles, healthcare facilities should implement a “first in, first out” (FIFO) system. Rotating stock ensures Blood Collection Needles and Medical Supplies Needles are used before their expiration date, reducing waste and maintaining consistent quality. Clearly labeled storage with visible expiration dates can simplify this process.
Handling Sterile Needles with bare hands can introduce microorganisms and compromise sterility. Staff should use gloves or other protective tools when accessing Blood Collection Needle packs. Minimizing direct contact with Medical Supplies Needles ensures that the products remain safe for clinical procedures.
Different types of Sterile Needles and Medical Supplies Needles should be organized by size and intended use. Separating Blood Collection Needles from other syringes or hypodermic supplies helps reduce errors and simplifies inventory management. Proper segregation also protects delicate packaging from damage caused by overcrowding.
Storage areas for Sterile Needles should be inspected regularly for dust, spills, or signs of moisture. Routine cleaning prevents the accumulation of contaminants that could affect Blood Collection Needles and other Medical Supplies Needles. Facilities should document inspections to ensure compliance with safety protocols.
Educating staff about proper handling and storage of Sterile Needles is essential. Training should emphasize careful opening of Blood Collection Needle packs, correct shelving practices, and adherence to expiration dates. Informed personnel are less likely to compromise the sterility of Medical Supplies Needles during daily operations.
When moving Sterile Needles between storage areas or departments, use dedicated transport boxes or containers to prevent damage and contamination. Blood Collection Needles and other Medical Supplies Needles should remain sealed during transport to preserve sterility until they reach their point of use.
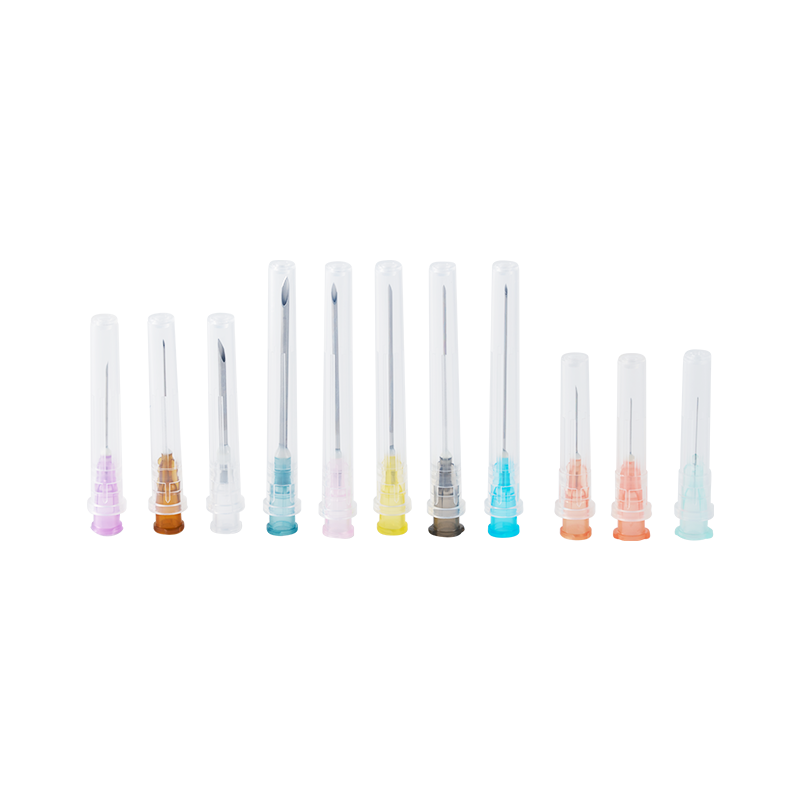

Proper storage of Sterile Needles, Blood Collection Needles, and Medical Supplies Needles is a key component of maintaining safety and operational efficiency in healthcare environments. By controlling environmental conditions, preserving original packaging, implementing stock rotation, minimizing direct contact, organizing by type, inspecting regularly, training staff, and using protective transport methods, facilities can effectively prevent contamination and ensure that needles remain sterile and ready for safe handling.
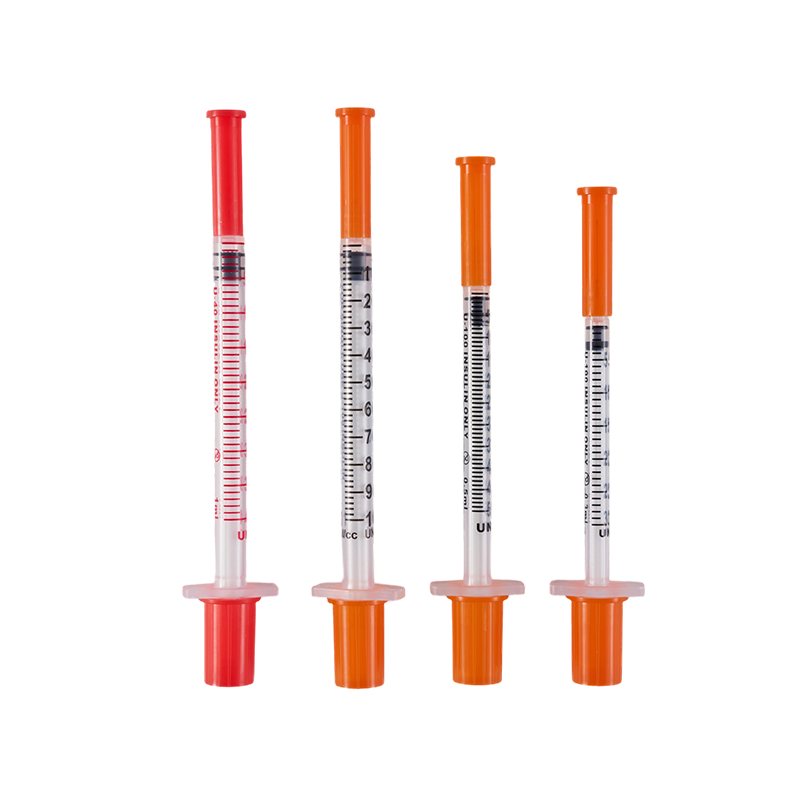
The design and production comply with ISO8537. The plastic parts are moulded by ...
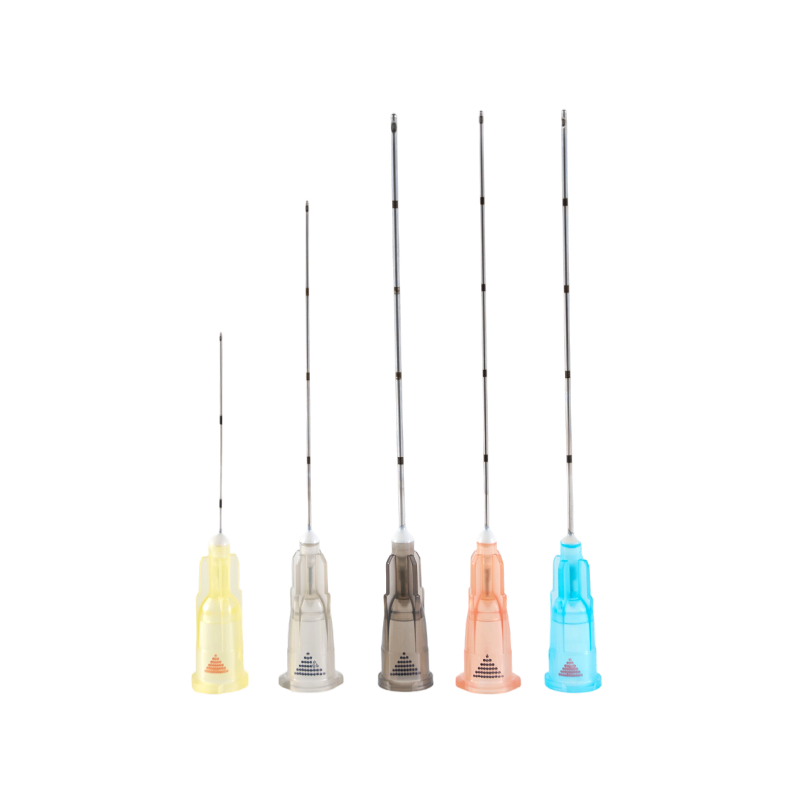

There are three kinds of the tip types, Sealed-circle with 2 side holes, sealed-...
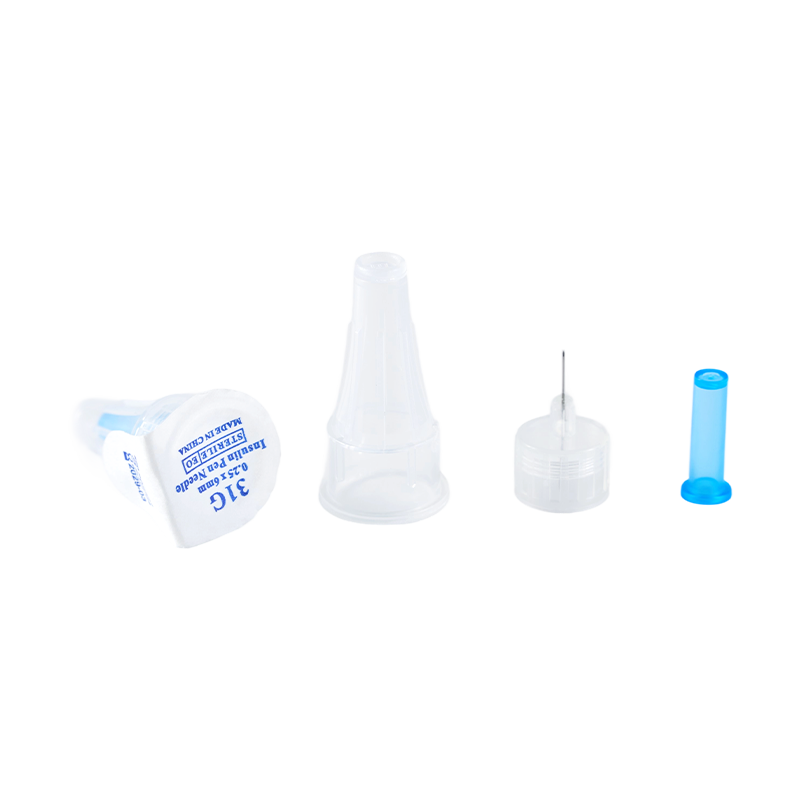

Assembling with insulin pen, for insulin hypodermic injection.The plastic parts ...
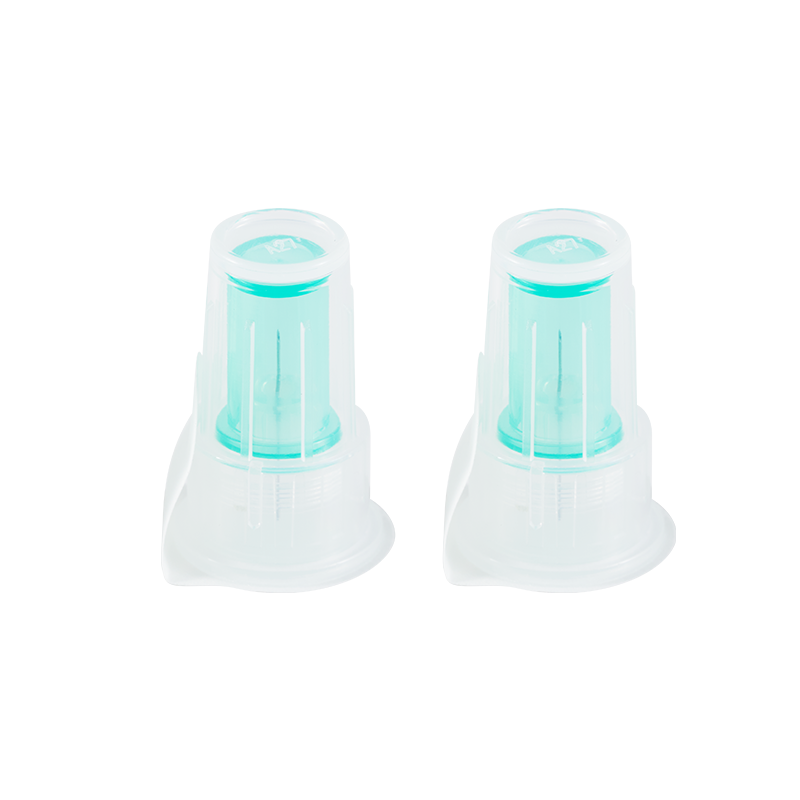

Used in conjunction with an insulin pen, it is used for subcutaneous injection o...

The cannula is made of high quality austenite stainless steel.All the components...
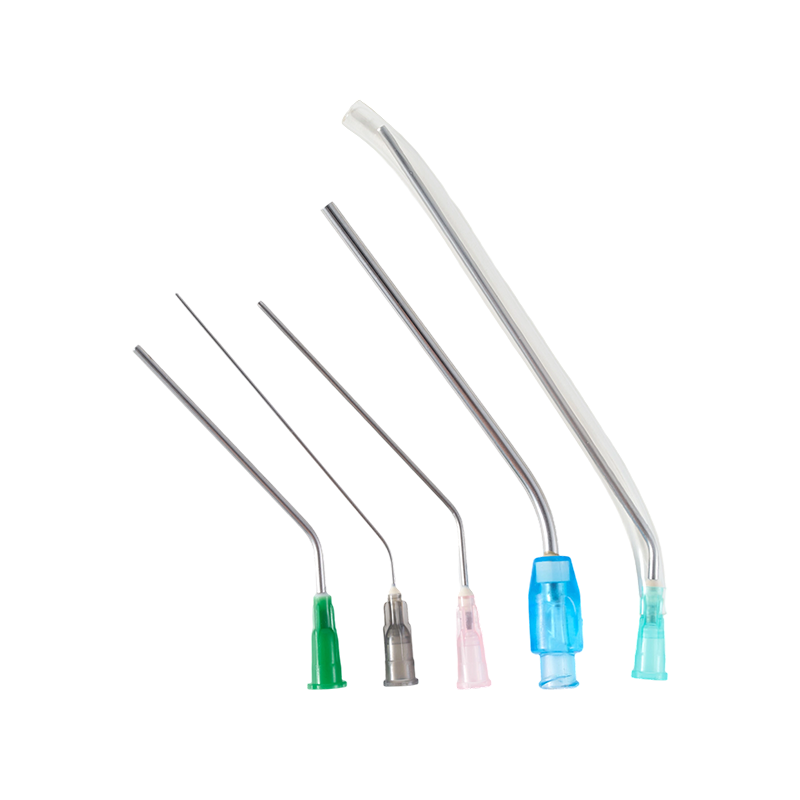
The material of the needle is Medical grade SUS304,which have great stiffness, t...
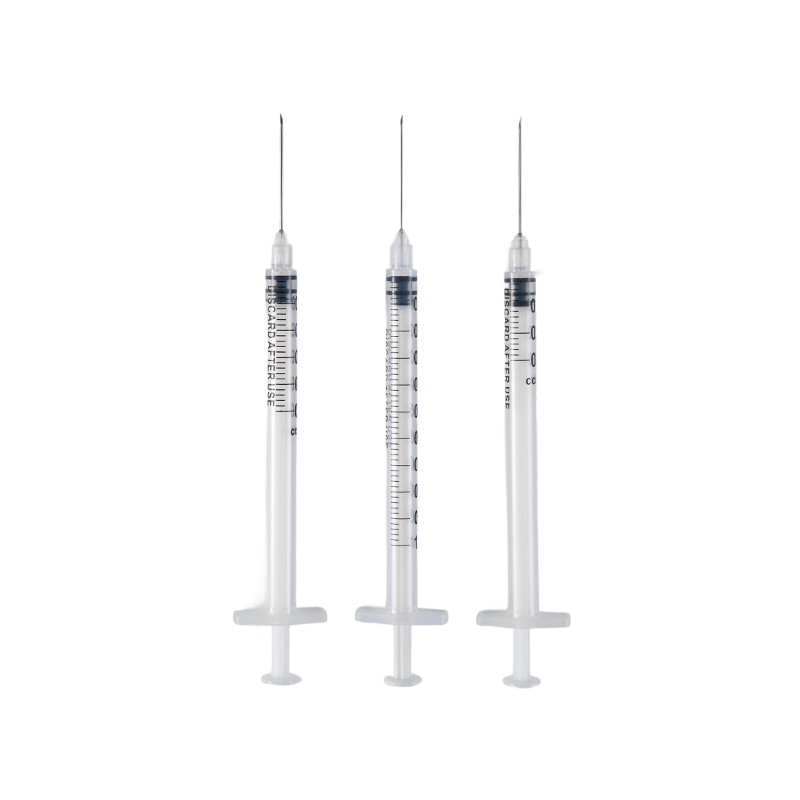
The barrel is made from high transparent polypropylene(PP),which have a bright a...
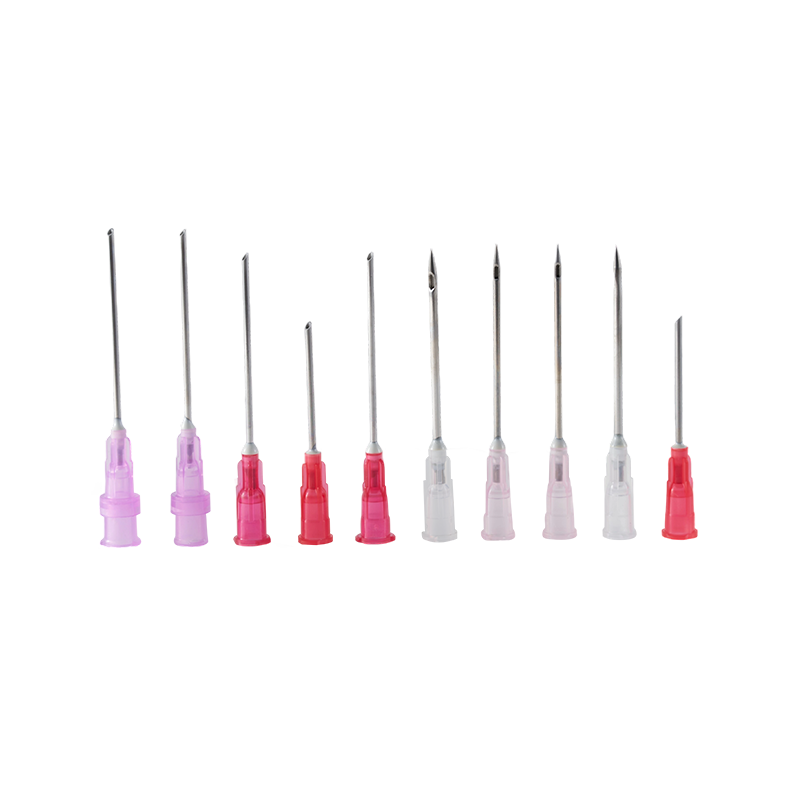

The cannula is made of high quality austenite stainless steel.The lancet tip is ...